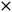接前一篇文章:
上一回讲解了pci_edu_realize函数中的pci_register_bar函数,本回开始对于edu设备的MMIO读写函数进行解析。
操作系统 与PCI设备交互的主要方式是PIO和MMIO。MMIO虽然是一段内存,但是其没有EPT映射,在 虚拟机 访问设备的MMIO时,会产生VM Exit;KVM识别此MMIO访问并且将该访问分派到应用层QEMU中;QEMU根据内存虚拟化的步骤进行分派,找到设备注册的MMIO读写回调函数;设备的MMIO读写回调函数根据设备的功能进行模拟,完成模拟之后可能会发送中断到虚拟机中,从而完成一些MMIO访问。
前文书( QEMU源码全解析 —— PCI设备模拟(5) )已经讲过,pci_edu_realize函数中调用memory_region_init_io函数,指定其读写函数是edu_mmio_ops。
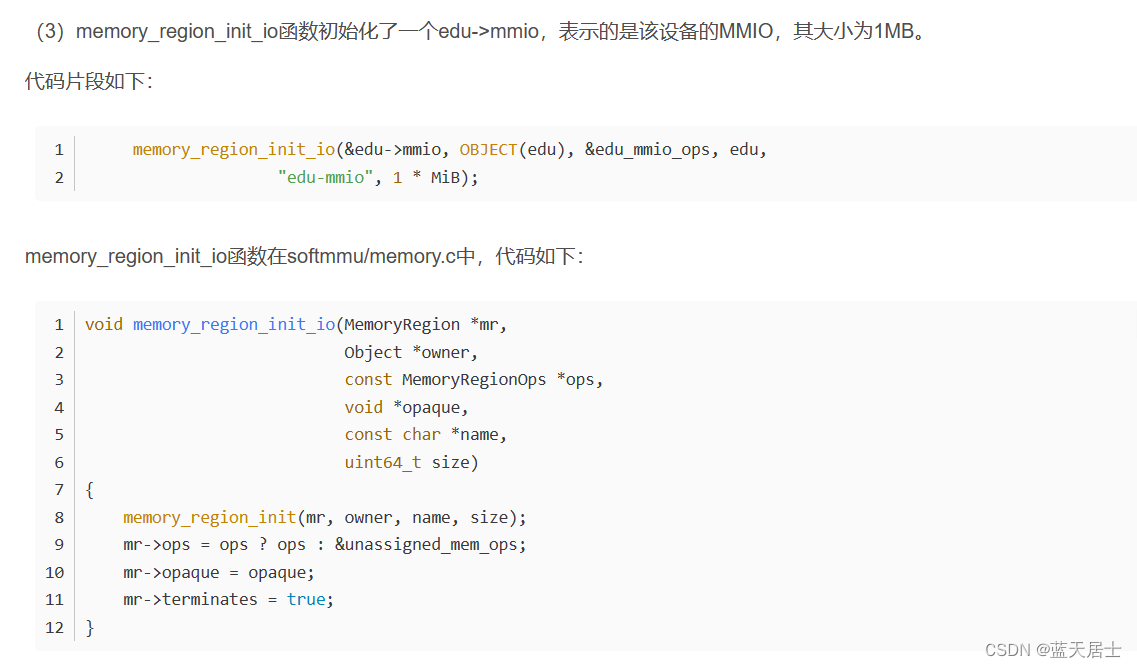
edu_mmio_ops在hw/misc/edu中初始化,代码如下:
- static const MemoryRegionOps edu_mmio_ops = {
- .read = edu_mmio_read,
- .write = edu_mmio_write,
- .endianness = DEVICE_NATIVE_ENDIAN,
- .valid = {
- .min_access_size = 4,
- .max_access_size = 8,
- },
- .impl = {
- .min_access_size = 4,
- .max_access_size = 8,
- },
-
- };
edu_mmio_ops的类型为MemoryRegionOps,此结构在include/exec/memory.h中定义,代码如下:
typedef struct MemoryRegionOps MemoryRegionOps;而struct MemoryRegionOps的定义也在include/exec/memory.h中,如下:
- /*
- * Memory region callbacks
- */
- struct MemoryRegionOps {
- /* Read from the memory region. @addr is relative to @mr; @size is
- * in bytes. */
- uint64_t (*read)(void *opaque,
- hwaddr addr,
- unsigned size);
- /* Write to the memory region. @addr is relative to @mr; @size is
- * in bytes. */
- void (*write)(void *opaque,
- hwaddr addr,
- uint64_t data,
- unsigned size);
-
- MemTxResult (*read_with_attrs)(void *opaque,
- hwaddr addr,
- uint64_t *data,
- unsigned size,
- MemTxAttrs attrs);
- MemTxResult (*write_with_attrs)(void *opaque,
- hwaddr addr,
- uint64_t data,
- unsigned size,
- MemTxAttrs attrs);
-
- enum device_endian endianness;
- /* Guest-visible constraints: */
- struct {
- /* If nonzero, specify bounds on access sizes beyond which a machine
- * check is thrown.
- */
- unsigned min_access_size;
- unsigned max_access_size;
- /* If true, unaligned accesses are supported. Otherwise unaligned
- * accesses throw machine checks.
- */
- bool unaligned;
- /*
- * If present, and returns #false, the transaction is not accepted
- * by the device (and results in machine dependent behaviour such
- * as a machine check exception).
- */
- bool (*accepts)(void *opaque, hwaddr addr,
- unsigned size, bool is_write,
- MemTxAttrs attrs);
- } valid;
- /* Internal implementation constraints: */
- struct {
- /* If nonzero, specifies the minimum size implemented. Smaller sizes
- * will be rounded upwards and a partial result will be returned.
- */
- unsigned min_access_size;
- /* If nonzero, specifies the maximum size implemented. Larger sizes
- * will be done as a series of accesses with smaller sizes.
- */
- unsigned max_access_size;
- /* If true, unaligned accesses are supported. Otherwise all accesses
- * are converted to (possibly multiple) naturally aligned accesses.
- */
- bool unaligned;
- } impl;
- };
其中的read和Write函数分别表示该MMIO的读写回调;endianness表示字节的大小端模式。
以write回调函数为例,
- /* Write to the memory region. @addr is relative to @mr; @size is
- * in bytes. */
- void (*write)(void *opaque,
- hwaddr addr,
- uint64_t data,
- unsigned size);
- static void edu_mmio_write(void *opaque, hwaddr addr, uint64_t val,
- unsigned size)
其原型中的opaque表示的是设备的对象;addr表示虚拟机读的地址在该MMIO中的偏移地址;data(val)表示要写入的值;size表示写入值的大小,通常由单字节、双字节、四字节以及八字节。
edu_mmio_write函数同样在hw/misc/edu.c中,代码如下:
- static void edu_mmio_write(void *opaque, hwaddr addr, uint64_t val,
- unsigned size)
- {
- EduState *edu = opaque;
-
- if (addr < 0x80 && size != 4) {
- return;
- }
-
- if (addr >= 0x80 && size != 4 && size != 8) {
- return;
- }
-
- switch (addr) {
- case 0x04:
- edu->addr4 = ~val;
- break;
- case 0x08:
- if (qatomic_read(&edu->status) & EDU_STATUS_COMPUTING) {
- break;
- }
- /* EDU_STATUS_COMPUTING cannot go 0->1 concurrently, because it is only
- * set in this function and it is under the iothread mutex.
- */
- qemu_mutex_lock(&edu->thr_mutex);
- edu->fact = val;
- qatomic_or(&edu->status, EDU_STATUS_COMPUTING);
- qemu_cond_signal(&edu->thr_cond);
- qemu_mutex_unlock(&edu->thr_mutex);
- break;
- case 0x20:
- if (val & EDU_STATUS_IRQFACT) {
- qatomic_or(&edu->status, EDU_STATUS_IRQFACT);
- /* Order check of the COMPUTING flag after setting IRQFACT. */
- smp_mb__after_rmw();
- } else {
- qatomic_and(&edu->status, ~EDU_STATUS_IRQFACT);
- }
- break;
- case 0x60:
- edu_raise_irq(edu, val);
- break;
- case 0x64:
- edu_lower_irq(edu, val);
- break;
- case 0x80:
- dma_rw(edu, true, &val, &edu->dma.src, false);
- break;
- case 0x88:
- dma_rw(edu, true, &val, &edu->dma.dst, false);
- break;
- case 0x90:
- dma_rw(edu, true, &val, &edu->dma.cnt, false);
- break;
- case 0x98:
- if (!(val & EDU_DMA_RUN)) {
- break;
- }
- dma_rw(edu, true, &val, &edu->dma.cmd, true);
- break;
- }
- }
edu_mmio_write函数展示了一个虚拟机在写设备MMIO地址时QEMU中设备模拟的典型行为。
(1)首先,需要检查读写地址以及大小是否在范围之内。代码片段如下:
- if (addr < 0x80 && size != 4) {
- return;
- }
-
- if (addr >= 0x80 && size != 4 && size != 8) {
- return;
- }
(2)然后,根据具体的地址来进行适当的行为。
这些行为可以是简单地设置一个值,如这里的写0x04地址,代码片段如下:
- case 0x04:
- edu->addr4 = ~val;
- break;
也可以是将中断设置为高电平(写0x60地址)或者设置为低电平(写0x64地址),代码片段如下:
- case 0x60:
- edu_raise_irq(edu, val);
- break;
- case 0x64:
- edu_lower_irq(edu, val);
- break;
还可以是通过dma读写设备虚拟机的物理地址(写0x80地址),代码片段如下:
- case 0x80:
- dma_rw(edu, true, &val, &edu->dma.src, false);
- break;
对于read回调函数,也是类似的机制。这里仅给出edu_mmio_read函数源码,在hw/misc/edu.c中,代码如下:
- static uint64_t edu_mmio_read(void *opaque, hwaddr addr, unsigned size)
- {
- EduState *edu = opaque;
- uint64_t val = ~0ULL;
-
- if (addr < 0x80 && size != 4) {
- return val;
- }
-
- if (addr >= 0x80 && size != 4 && size != 8) {
- return val;
- }
-
- switch (addr) {
- case 0x00:
- val = 0x010000edu;
- break;
- case 0x04:
- val = edu->addr4;
- break;
- case 0x08:
- qemu_mutex_lock(&edu->thr_mutex);
- val = edu->fact;
- qemu_mutex_unlock(&edu->thr_mutex);
- break;
- case 0x20:
- val = qatomic_read(&edu->status);
- break;
- case 0x24:
- val = edu->irq_status;
- break;
- case 0x80:
- dma_rw(edu, false, &val, &edu->dma.src, false);
- break;
- case 0x88:
- dma_rw(edu, false, &val, &edu->dma.dst, false);
- break;
- case 0x90:
- dma_rw(edu, false, &val, &edu->dma.cnt, false);
- break;
- case 0x98:
- dma_rw(edu, false, &val, &edu->dma.cmd, false);
- break;
- }
-
- return val;
- }
欲知后事如何,且看下回分解。










 本文深入解析QEMU中PCI设备模拟的MMIO读写回调函数,介绍了MemoryRegionOps结构及其实现的读写操作。在虚拟机访问设备MMIO时,QEMU会调用相应的回调函数进行模拟处理,如设置值、触发中断或进行DMA操作。
本文深入解析QEMU中PCI设备模拟的MMIO读写回调函数,介绍了MemoryRegionOps结构及其实现的读写操作。在虚拟机访问设备MMIO时,QEMU会调用相应的回调函数进行模拟处理,如设置值、触发中断或进行DMA操作。